Commuting in large cities every day indeed takes a lot of your time, not to mention how it impacts your health in the long run. The fact is that air pollution in many major cities in Asia is reaching alarming heights. This leads to various respiratory system illnesses that are very dangerous and even downright deadly.
Chronic respiratory diseases are diseases of the airways and other structures of the lung. Some of the most common are: asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), occupational lung diseases and pulmonary hypertension. According to WHO, there are approximately 7 million deaths worldwide per year from air pollution; two-thirds of them occur in Asia.
Many times, people are genetically more likely to get respiratory conditions, but your work place or environmental exposures could also play a big role. One thing is for sure, SMOKING is the most common cause of respiratory disease.
Today, we will learn more about the top chronic respiratory diseases and how to prevent and cure the illnesses.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a common lung disease caused by an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or mucus, causing cough with mucous secretion, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia. Pneumonia can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening. It’s more serious for infants and young children, people older than age 65, and people with health problems or weakened immune systems.
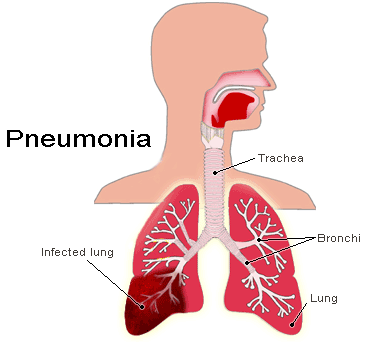
It’s very important for adults over 65 or those with other chronic disease to get the pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. Additional suggested ways to prevent this respiratory condition include washing hands frequently and getting the flu shot.
Asthma
Asthma is one of the major noncommunicable diseases. It is defined as a common, chronic respiratory condition that causes difficulty breathing due to inflammation of the airways. The strongest risk factors for developing asthma are a combination of genetic predisposition with environmental exposure to inhaled substances and particles that may provoke allergic reactions or irritate the airways, such as: indoor allergens (house dust mites in bedding, carpets and stuffed furniture), outdoor allergens (pollens), tobacco smoke, chemical irritants in the workplace, or air pollution. Other triggers can include cold air, extreme emotional arousal such as anger or fear, and physical exercise.

Symptoms may occur several times in a day or week in affected individuals, and for some people become worse during physical activity or at night. During an asthma attack, the lining of the bronchial tubes swells, causing the airways to narrow and reducing the flow of air into and out of the lungs.
Although asthma cannot be cured, appropriate management can control the disease and enable people to enjoy a good quality of life. Medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are needed to control the progression of severe asthma. It’s also important to avoid asthma triggers – stimuli that irritate and inflame the airways.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is not one single disease but an umbrella term used to describe several respiratory illnesses that cause breathlessness, or the inability to exhale normally. The most common symptoms of COPD are breathlessness, or a ‘need for air’, excessive mucus production, and a chronic cough. However, COPD is not just simply a “smoker’s cough”, but an under-diagnosed, life threatening lung disease that may progressively lead to death. The disease usually begins while people are in their 30s or 40s and then peaks during their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
The causes for COPD have opposite patterns according to the geographic areas. In high and middle-income countries, tobacco smoke is the biggest risk factor, meanwhile in low-income countries, exposure to indoor air pollution, such as the use of biomass fuels for cooking and heating, causes the COPD burden.
Many cases of COPD are preventable by avoidance or early termination of smoking. COPD is not curable, but treatment can relieve symptoms, improve quality of life and reduce the risk of death.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is one type of COPD emphasized by a chronic cough. Usually people cough up mucus from the lungs, especially in the morning. This happens because mucus glands in the airways increase output, and patients have to cough that extra secretion out. Since chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD, it’s treated the same way.
Treatment can help with your symptoms. It often includes medicines to open your airways and help clear away mucus. You may also need oxygen therapy. Pulmonary rehabilitation may help you manage better in daily life.
Emphysema
Emphysema is a serious respiratory disease, which is another form of COPD. The most common cause is smoking. Those who suffer from emphysema have trouble exhaling air from their lungs. Cigarette smoke damages the air sacs in the lungs to a point where they can no longer repair themselves. Over time, the inner walls of the air sacs weaken and rupture – creating larger air spaces instead of many small ones. This reduces the surface area of the lungs and, in turn, the amount of oxygen that reaches your bloodstream. Emphysema evolves slowly over the years, and
there is no cure; however, those who quit smoking are more likely to see the disease’s progression slow. Wear a mask to protect your lungs if you work with chemical fumes or dust.

Lung Cancer
With the ability to develop in any part of the lungs, this cancer is difficult to detect. Most often, the cancer develops in the main part of the lungs near the air sacs. DNA mutations in the lungs cause irregular cells to multiply and create an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells, or a tumor. These tumors interfere with the regular functions of the lungs.
People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer, though lung cancer can also occur in people who have never smoked. The risk of lung cancer increases with the length of time and number of cigarettes you’ve smoked. Symptoms can take years to appear, but include things like chronic coughing, changes in voice, harsh breathing sounds and coughing up blood.

Not all lung cancers can be prevented. But there are things you can do that might lower your risk, such as terminating tobacco, avoiding radon, limiting exposure to cancer-causing chemicals, and practicing a healthy diet.
Cigarette smoking either causes or worsens every respiratory disease on this list. The Center for Disease Control and Prevent (CDC) says tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable illness and death and produces 480,000 deaths a year (including deaths from secondhand smoke). Practice avoidance in order to prevent respiratory disease, that includes avoiding sick people and places with a lot of dust or harsh chemicals. Try to maintain a healthy weight, get adequate sleep, decrease stress, add plenty of activity and eat a balanced diet.
References: